Blood Pressure:
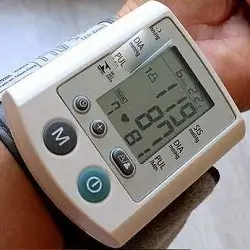 Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as it is pumped by our heart. It is measured in two ways- Systolic pressure and Diastolic pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as it is pumped by our heart. It is measured in two ways- Systolic pressure and Diastolic pressure
Systolic pressure: the pressure when the heart beats and pushes blood out. The range of systolic blood pressure can be categorized as follows:
Normal: Less than 120 mmHg
Elevated: 120-129 mmHg
Stage 1 Hypertension: 130-139 mmHg
Stage 2 Hypertension: 140 mmHg or higher
Diastolic pressure: the pressure when the heart relaxes between beats. The range of diastolic blood pressure can also be categorized as follows:
Normal: Less than 80 mmHg
Elevated: 80-89 mmHg
Stage 1 Hypertension: 90-99 mmHg
Stage 2 Hypertension: 100 mmHg or higher
Role of blood pressure:
Delivering oxygen and nutrients: Blood pressure ensures the flow of blood efficiently through our arteries, delivering oxygen and nutrients to all the parts of our body. This supports essential functions like cell repair, growth, and waste removal.
Maintaining body temperature: The blood circulation helps regulate our body temperature by distributing heat throughout the body.
Filtering waste products: Blood pressure helps filter waste products from our body through the kidneys.
Fighting infections: Blood carries white blood cells, which help in fighting infections.
Promoting healthy organ function: Adequate blood pressure ensures proper blood flow to vital organs like the heart, brain, and kidneys, enabling them to function properly.
Effects of abnormal blood pressure:
High blood pressure (hypertension): This increases the risk of heart attacks, kidney failure, strokes, and other health problems.
Low blood pressure (hypotension): This may cause fainting, dizziness, fatigue, and other symptoms.
Several lifestyle factors can help maintain balanced blood pressure:
Healthy diet: Reduce and minimize salt intake, eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and limit saturated and unhealthy fats.
Regular exercise: Aim for regular moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Maintain a healthy weight: The body weight in excess can put strain on the heart and arteries.
Managing stress: Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.
Limiting alcohol and caffeine: Excessive consumption can increase the blood pressure.
Quitting smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Regular monitoring the blood pressure: This method can detect any abnormalities and timely intervention to the problem.
The importance of understanding the blood pressure and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing health problems and improve the overall health well-being.
Supplements to reduce hypertension:
Several supplements may potentially decrease hypertension, although it’s always essential to consult with a healthcare professional before consuming any supplements, especially under medical conditions or you are on medications.
Here are some examples of supplements and ingredients with evidence suggesting potential benefits for lowering blood pressure:
Potassium, Magnesium, Omega-3 fatty acids, Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), Garlic, Hibiscus sabdariffa, Probiotics, Calcium, Vitamin D, Folic acid
Supplements should never replace a healthy lifestyle for managing blood pressure. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential for controlling hypertension.
Plant based Oils and seeds:
